Imagine your industrial machinery suddenly stops working. Often, improper bearing selection causes these failures, making up about 10% of all premature breakdowns. When you choose ball bearings or Roller Bearings, you shape the reliability and efficiency of your equipment. RMO Bearings gives you advanced solutions that boost durability and performance.
|
Feature |
Benefit |
Impact on Reliability |
|---|---|---|
|
Durability |
Resists wear, extends service life |
Fewer unexpected failures |
|
Low friction |
Minimizes heat, supports high speeds |
Enhances continuous operation |
|
High load capacity |
Reliable in heavy-duty settings |
Maintains equipment reliability |
You get access to specialized and customizable options from RMO Bearings, including expert support and tailored recommendations.
Key Takeaways
-
Choose roller bearings for heavy-duty applications. They handle higher loads and provide better durability in tough environments.
-
Select ball bearings for high-speed operations. Their design minimizes friction, making them ideal for applications where speed is crucial.
-
Consider the type of load your machinery will face. Roller bearings excel with radial loads, while ball bearings suit lighter loads.
-
Regular maintenance is key. Follow recommended schedules for lubrication and cleaning to extend the lifespan of your bearings.
-
Consult with experts like RMO Bearings for customized solutions. Tailored bearings can improve performance and reduce downtime.
Types of Bearings in Industrial Machinery
When you look at the main types of bearings used in industrial machinery, you will notice two stand out: ball bearings and roller bearings. These two types of bearings play a crucial role in keeping your equipment running smoothly and efficiently.
Ball Bearings Overview
Ball bearings are the most widely produced type, making up over 60% of the global market. You will find ball bearings in everything from automotive engines to aerospace components. Their design uses small, hardened steel balls that roll between two smooth rings. This setup reduces friction and allows for high-speed rotation. Ball bearings work best when you need to support light to moderate loads and want to minimize heat buildup. Many industries rely on ball bearings because they are versatile and easy to maintain.
Roller Bearings Overview
Roller bearings account for a significant share of the market, especially in heavy-duty applications. These bearings use cylindrical, tapered, spherical, or needle-shaped rollers instead of balls. The larger contact area of roller bearings lets you handle higher radial loads and more demanding conditions. You will often see roller bearings in construction equipment, conveyor systems, and large motors. RMO Bearings offers a wide range of roller bearings, including cylindrical, tapered, and spherical types. You can also request custom roller bearings to fit your specific needs.
Key Components and Function
Both ball bearings and roller bearings share some basic parts:
-
Inner ring
-
Outer ring
-
Rolling elements (balls or rollers)
-
Cage to keep the elements spaced
Tip: Choosing the right types of bearings for your machinery can improve performance and reduce downtime.
You can select from many types of bearings, but ball bearings and roller bearings remain the most common. RMO Bearings provides both standard and customizable options, so you always have the right solution for your equipment.
Roller Bearings vs. Ball Bearings: Design Differences
Contact Area and Shape
When you compare roller bearings and ball bearings, the most important difference lies in the shape of their rolling elements and the way they contact the raceways. Roller bearings use cylindrical, tapered, spherical, or needle-shaped rollers. These rollers create a line contact with the race. In contrast, ball bearings use small, hardened steel balls that form a point contact with the race.
This difference in contact area has a big impact on performance. The line contact in roller bearings gives you a much larger surface area for load distribution. This design lets roller bearings support heavier loads without deforming. Ball bearings, with their point contact, have a smaller contact area. This limits their ability to handle heavy loads, but it allows them to operate smoothly at higher speeds.
-
Roller bearings have a line contact, providing a larger surface area for load distribution.
-
Ball bearings operate on a point contact, resulting in a smaller contact area and limited load capacity.
-
This difference makes roller bearings more suitable for heavier radial loads compared to ball bearings.
The larger contact area in roller bearings spreads the force over a wider region. This feature makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications in industrial machinery. Ball bearings, on the other hand, work best when you need to support light to moderate loads and want to minimize friction.
Note: The shape and contact area of the rolling elements directly affect how much weight each bearing can handle and how long it will last.
Friction and Movement
Friction plays a key role in how both roller bearings and ball bearings perform. Both types use rolling elements to reduce sliding friction, which is much higher than rolling friction. However, the shape and contact area of the rolling elements influence the amount of friction each bearing produces.
You can see the difference in friction coefficients in the table below:
|
Bearing Type |
Coefficient of Friction |
|---|---|
|
Deep groove ball bearings |
0.0015-0.003 |
|
Self-aligning ball bearings |
0.0010-0.0010 |
|
Single row angular contact ball bearings |
0.0015-0.002 |
|
Double row angular contact ball bearings |
0.0024-0.003 |
|
Cylindrical roller bearings |
0.0010-0.003 |
|
Needle bearings |
0.0020 |
|
Self-aligning roller bearings |
0.0020-0.003 |
|
Tapered roller bearings |
0.0020-0.005 |
|
Thrust ball bearings |
0.0012 |
|
Thrust self-aligning roller bearings |
0.003 |
|
Thrust cylindrical roller bearings |
0.004 |
|
Thrust needle bearings |
0.004 |
You can also compare the average friction coefficients for each type:
|
Bearing Type |
Friction Coefficient |
|---|---|
|
Ball Bearing |
0.001–0.0015 |
|
Roller Bearing |
0.002–0.004 |
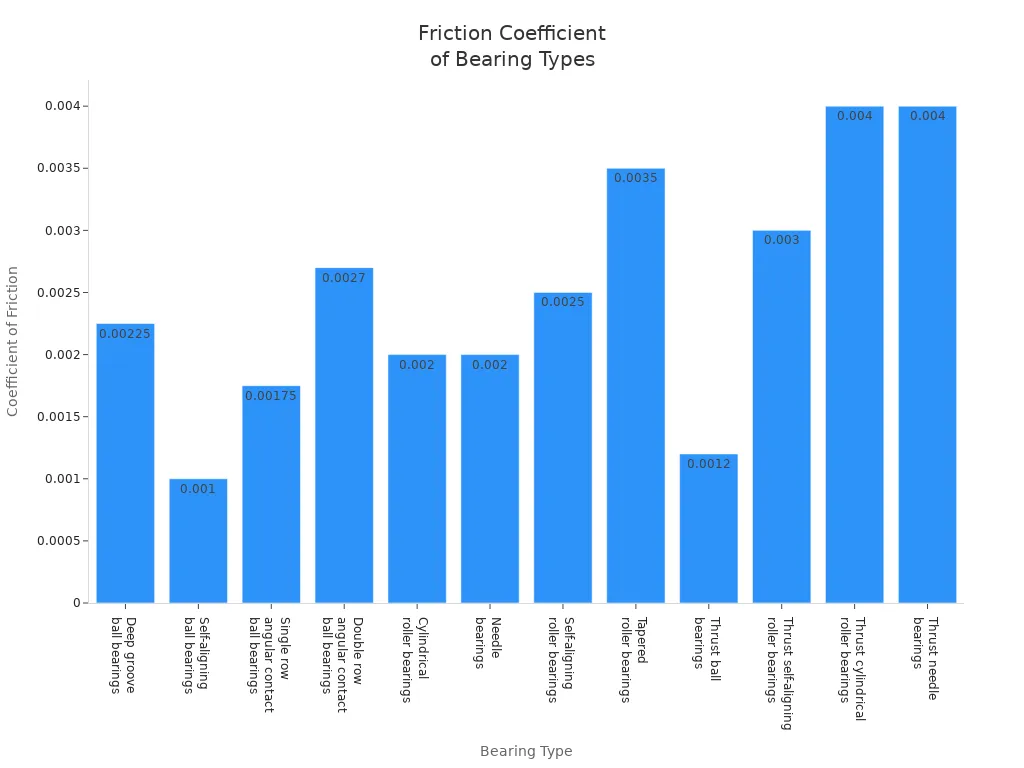
Ball bearings usually have a lower coefficient of friction than roller bearings. This means ball bearings generate less heat and can run at higher speeds. You will often choose ball bearings for applications where speed matters more than load capacity. Roller bearings, with their larger contact area, produce slightly more friction. However, this extra friction is a trade-off for their ability to handle greater radial loads and moderate thrust loads.
In high-speed machinery, both types of bearings reduce friction compared to sliding surfaces. Ball bearings excel in high-speed settings because their point contact keeps friction low. Roller bearings, while not as fast, give you the strength to support heavy radial loads and some axial load. The design and material of each bearing also affect how well it performs under different speeds and loads.
Tip: When you select a bearing for your equipment, always consider the balance between speed, load capacity, and friction. Ball bearings are best for high-speed, light-load applications. Roller bearings are the top choice for heavy-duty, high-load environments.
Load Capacity and Performance
Radial and Axial Loads
When you select bearings for industrial machinery, you need to consider how they handle different types of forces. Radial loads push outward from the center of the bearing, while axial loads push along the axis. Roller bearings excel at managing both, especially when you deal with heavy loads. Their design uses rollers that create a larger contact area, which spreads the force more evenly.
-
Roller bearings are specifically designed to handle heavy loads and impacts, making them ideal for industrial applications.
-
They have a high load capacity due to a larger contact area that distributes the load evenly, minimizing wear.
-
Roller bearings operate at lower temperatures compared to ball bearings, reducing the risk of overheating.
-
Ball bearings, on the other hand, have a limited load capacity and are susceptible to damage under sudden heavy loads.
Ball bearings work well for lighter radial and axial loads. Their point contact design allows for smooth movement, but it limits the amount of force they can handle. If your equipment faces frequent shocks or heavy loads, roller bearings give you the strength and reliability you need.
Tip: Always match the bearing type to the expected load conditions for longer equipment life.
Durability and Lifespan
You want your bearings to last, especially in tough environments. Roller bearings outperform ball bearings in durability under heavy loads due to their cylindrical shape, which allows for better stress distribution. This feature means you can rely on roller bearings in settings with high vibration or dust.
-
Roller bearings provide enhanced durability in harsh environments, such as those with high vibration.
-
The durability of roller bearings is particularly beneficial in environments exposed to dust or high vibration.
Ball bearings offer good performance in clean, low-vibration settings. However, when you need maximum durability and a long lifespan, roller bearings stand out. Their robust construction and superior load capacity make them the preferred choice for demanding industrial machinery.
Speed and Efficiency
Maximum Speeds
You need to consider speed when choosing between roller bearings and ball bearings for your equipment. Ball bearings often reach higher speeds because their point contact design reduces friction. This makes them a popular choice for electric motors and fans. Roller bearings, with their line contact, handle more load but usually operate at lower speeds. However, some advanced roller bearings can still achieve impressive speeds, especially in heavy machinery.
Here is a table showing the maximum speeds for different bearing types in industrial machinery:
|
Bearing Type |
Maximum Speed (RPM) |
|---|---|
|
Ball, Deep Groove |
500,000 |
|
Ball, Angular Contact |
450,000 |
|
Cylindrical, 2 Piece Brass Cage |
550,000 |
|
2 Piece Steel Cage |
450,000 |
|
Stamped Steel Cage |
330,000 |
|
1 Piece Brass Cage |
600,000 |
|
Full Complement |
170,000 |
|
Tapered Roller, Pin Type Cage |
400,000 |
|
Brass, Land Riding Cage |
450,000 |
|
Spherical, Brass Finger Cage |
220,000 |
|
Ball, BT |
200,000 |
|
Cylindrical, 2 Piece Cage |
220,000 |
|
Tapered Roller, 2 Piece Cage |
180,000 |
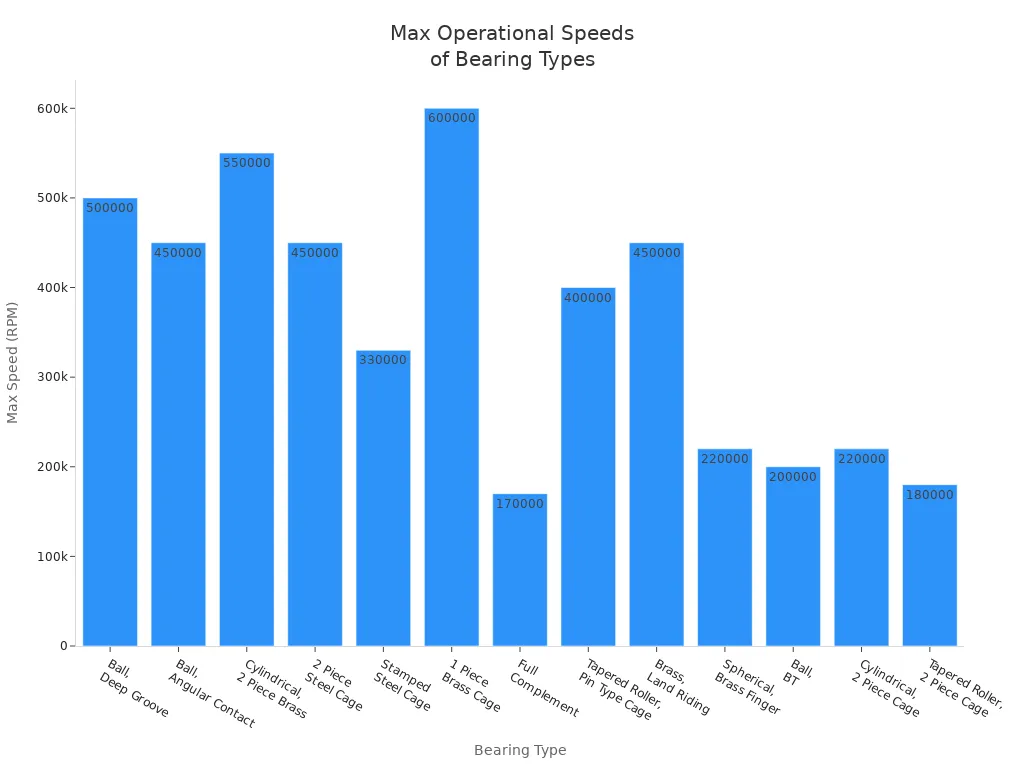
Ball bearings excel in high-speed applications. Roller bearings work best in heavy machinery where load capacity matters more than speed.
Heat and Maintenance
When you run equipment at high speeds, heat becomes a concern. Ball bearings generate less heat because they have lower friction. This helps your machines run smoothly and reduces energy loss. Roller bearings, used in heavy machinery, handle more stress and may produce more heat. You need to use advanced lubrication systems to keep them cool and efficient.
-
High-speed bearings use special materials and precise manufacturing to reduce friction and heat.
-
Lubrication systems, like air-oil lubrication, help keep bearings cool and prevent wear.
-
Bearings in heavy machinery must withstand high temperatures and heavy loads.
Maintenance also differs between the two types. Ball bearings require regular lubrication, cleaning, and careful handling. Roller bearings, especially in heavy machinery, need more frequent lubrication and cleaning because they face higher loads and stress.
|
Bearing Type |
Maintenance Requirements |
Applications |
|---|---|---|
|
Ball Bearings |
Require regular lubrication, cleaning, and proper handling to prevent wear and failure. |
Electric motors, fans, automotive |
|
Roller Bearings |
Need more frequent lubrication and cleaning due to higher load capacities and stress. |
Conveyor belts, mining equipment, heavy machinery |
Tip: Always follow the recommended maintenance schedule for your bearings. This helps you avoid unexpected downtime and keeps your industrial machinery running at peak efficiency.
Types of Roller Bearings
You will find several types of roller bearings in industrial machinery. Each type offers unique features that help you solve specific engineering challenges. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right bearing for your equipment.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical roller bearings handle heavy radial loads with ease. You can use them in conveyor systems and automotive transmissions. These bearings come in single-row and double-row designs, so you can match them to your speed and load requirements. Manufacturers use materials like high-carbon chrome steel or stainless steel, which lets you use these bearings in different environments. The design diversity allows cylindrical roller bearings to work well in heavy machinery and wind power generation.
-
Handle heavy radial loads
-
Available in single-row and double-row designs
-
Adapt to various environments with different materials
-
Suitable for heavy machinery and wind power
Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings give you superior load capacity. The tapered shape creates a larger contact area, which distributes loads more effectively. You get a compact design that saves space in your machinery. These bearings offer precision operation, so you see less wear and longer service life. You can adjust the clearance, which helps you tune performance and simplify maintenance. RMO Bearings offers the 30306 Tapered Roller Bearings, which deliver premium performance in single-row tapered applications.
-
Superior load capacity with tapered design
-
Compact and space-saving
-
Precision operation for reduced wear
-
Adjustable clearance for optimal performance
Spherical Roller Bearings
Spherical roller bearings work well in applications where you need to handle both heavy loads and misalignment. The 22318CC/W33 Spherical Roller Bearing from RMO Bearings is a popular choice. You see these bearings in many industries, including paper-making machinery, railway vehicle axles, rolling mill gearboxes, crushers, vibrating screens, and woodworking machinery.
|
Application Type |
|---|
|
Paper-making machinery |
|
Railway vehicle axles |
|
Rolling mill gearboxes |
|
Crushers |
|
Vibrating screens |
|
Printing machinery |
|
Woodworking machinery |
|
Industrial reducers |
|
Vertical bearing-mounted self-aligning bearings |
Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings help you design compact machinery with high load-carrying capacity. You can use them in radially tight spaces. The X-life configuration gives you up to 50% longer service life because of improved surface quality. These bearings offer higher performance, reduced friction, and lower temperatures, which means greater efficiency for your equipment.
-
Radially compact design for tight spaces
-
High load-carrying capacity
-
Longer service life with X-life configuration
-
Greater efficiency with reduced friction and lower temperatures
Tip: When you select roller bearings, always consider the specific needs of your machinery. RMO Bearings provides a wide range of options, including customizable solutions for unique industrial challenges.
Choosing the Right Bearing
Application Factors
Selecting the right bearing for your industrial machinery requires careful analysis. You need to match the bearing type to your specific application. Start by considering the forces your equipment will face. Some machines need to handle heavy radial loads, while others require support for axial or combined loads. Roller bearings excel in environments where you expect intense radial forces or frequent shocks.
You should also think about the precision your application demands. High-precision machinery, such as CNC tools or robotics, needs bearings with tight tolerances. Bearings with a tolerance level of 5 or higher ensure accurate shaft rotation and smooth operation. Speed is another critical factor. Some applications, like high-speed motors, need bearings designed for rapid rotation. Ball bearings often suit these needs, but advanced roller bearings can also perform well in certain high-speed settings.
Temperature and environmental conditions play a big role in bearing selection. If your machinery operates in extreme heat or cold, choose bearings that can withstand those temperatures. Specialized lubricants and cooling systems help maintain performance. In manufacturing plants, contamination from dust, moisture, or chemicals can cause premature bearing failure. Sealed or shielded roller bearings protect against these threats and extend service life.
Here is a table summarizing the main factors you should consider:
|
Factor |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Load |
Bearings must handle radial, axial, and combined loads effectively. |
|
Tolerance |
High precision applications require bearings with a tolerance level of 5 or higher. |
|
Speed |
Different bearings are optimized for specific speed ranges; high-speed applications need special designs. |
|
Temperature |
Bearings must be suitable for the temperature conditions they will encounter, including lubrication needs. |
|
Rotation Accuracy |
High tolerance bearings are necessary for applications where shaft rotation accuracy is critical. |
|
Rigidity |
The stiffness of bearings can significantly impact performance in certain machinery. |
|
Friction Torque |
Ball bearings generally have lower friction resistance compared to roller bearings, affecting efficiency. |
Note: Environmental factors such as temperature and contamination can lead to premature bearing failure. Extreme temperatures require bearings that can withstand these conditions. Moisture and contaminants may cause corrosion and wear, which affects the performance and lifespan of your bearings.
You can also take steps to protect your bearings in harsh environments:
-
Select bearings with appropriate temperature ranges.
-
Use specialized high or low-temperature bearings.
-
Choose lubricants designed for your operating conditions.
-
Implement cooling or heating systems to regulate temperature.
-
Use corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or ceramic.
-
Apply corrosion-resistant coatings and sealing to prevent moisture ingress.
-
Utilize sealed or shielded bearings to guard against contamination.
When you evaluate these factors, you make informed decisions that improve reliability and reduce downtime in your facility.
Custom Solutions from RMO Bearings
Every industrial application has unique requirements. Standard bearings may not always fit your machinery perfectly. RMO Bearings offers a wide range of customization options to help you achieve the best performance. You can request non-standard sizes or ultra-compact designs to fit tight spaces. Material selection is also flexible. Choose from chrome steel, stainless steel, or ceramic hybrid options to match your environment.
RMO Bearings provides different cage types, including steel, polyamide, and brass, to suit various applications. You can select specialized lubrication and coatings, such as high-temperature grease or anti-corrosion treatments, to extend bearing life. Sealing solutions, like single or double seals, protect against dust and water.
Here is a table showing the customization options available:
|
Customization Aspect |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Sizes & Dimensions |
Non-standard sizes, ultra-compact designs |
|
Materials |
Chrome steel, stainless steel, ceramic hybrid |
|
Cage Types |
Steel, polyamide, brass |
|
Lubrication & Coatings |
High-temp grease, anti-corrosion treatments |
|
Sealing Solutions |
Single & double sealing for dust/water protection |
When you choose custom roller bearings from RMO Bearings, you gain several advantages:
|
Benefit |
Description |
|---|---|
|
High Load Capacity |
RMO bearings are designed to handle intense radial loads and shocks, essential for industrial applications. |
|
Low Friction |
The linear contact design minimizes friction and heat generation, supporting stable operation. |
|
Durability |
RMO products are built to withstand demanding environments, ensuring longevity and reliability. |
|
Reduced Maintenance Needs |
Fewer replacements and lower maintenance requirements lead to cost savings and improved performance. |
|
Application Flexibility |
A wide range of bearing types and precision grades allows for tailored solutions to specific machinery. |
|
Improved Uptime |
Facilities have reported enhanced operational uptime after switching to RMO bearing solutions. |
Tip: Custom roller bearings from RMO Bearings help you solve complex engineering challenges. You can improve operational efficiency, reduce maintenance, and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
You can rely on RMO Bearings for expert guidance and support. The team works with you to design and deliver roller bearings that meet your exact needs. With a focus on quality and innovation, RMO Bearings helps you keep your machinery running smoothly, even in the most demanding industrial environments.








 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported
